This theory developed by B.F. Skinner is a behavioral theory that focuses on how consequences influence behavior. It emphasizes that behaviors can be shaped and maintained through reinforcement, which can be positive or negative. Reinforcement can be classified into the following types:
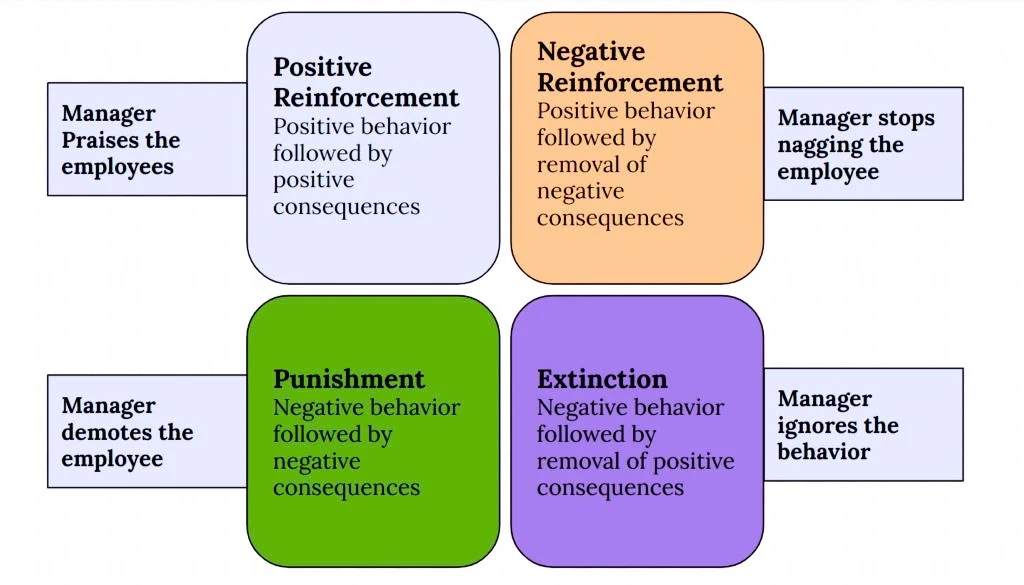
- Positive Reinforcement:
- Adding a rewarding stimulus after a desired behavior occurs.
- Example: Giving employees a bonus for achieving their targets encourages them to continue performing well.
- Negative Reinforcement:
- Removing an unpleasant stimulus when a desired behavior occurs.
- Example: Reducing supervision when employees meet their performance goals can motivate them to maintain that level of performance.
- Punishment:
- This involves introducing an adverse consequence to decrease the likelihood of an undesirable behavior. There are two types of punishment:
- Positive Punishment:
- Adding an unpleasant consequence following a behavior, such as giving a warning for poor performance.
- Negative Punishment:
- Taking away a positive stimulus, such as revoking privileges for not meeting expectations.
Extinction:
This occurs when a behavior is no longer reinforced, leading to a decrease in that behavior over time.
Example: If employees no longer receive recognition for good work, they may stop putting in extra effort.